Examining Skills Mismatch in the Tanzanian Formal Labour Market
Downloads
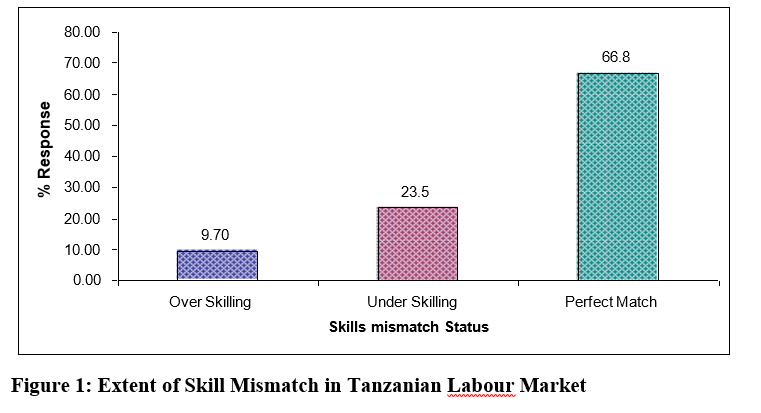
This study examined the pattern of skills mismatch in both private and public labour markets in Tanzania while taking Dar es Salaam and Dodoma regions as the areas of study. It employed cross sectional survey to collect primary from 319 workers who were selected by multistage sampling. Data were analyzed in SPSS using Multinomial logit model and Pearson Chi square. The study found out that 33.2% of employed workers are working in a circumstance of significant skills mismatch. Out of these, 9.7 % are underskilled and 23.5 % are over-skilled. In terms of sex, about 67.7 percent and 32.3 percent of males and females respectively were over skilled. This huge unqualified labour force could have a potential negative impact on the economy of Tanzania. This phenomenon therefore calls for a holistic skills upgrading and updating mechanism to be in place to align with the labour market standards